Technologies used
Overview
I was working a little with Fastendpoints and .Net core for building an API for a personal project I’ve been building. One of the requirements is the ability to upload a file via an API. I put together a basic sample on how to do this. This purley uploads a file, but doesn’t have any security as I wanted to just focus on the uploading. We’ll leave that for another post.
Let’s get started!
First we want to create a base .Net web application. We can do that by executing the command dotnet new web
dotnet add package FastEndpointsNext is we need to add the Fastendpoints package to the project. Make sure you at a terminal prompt and in the project directory. Once you are there you can execute the following command.
dotnet add package FastEndpointsNow that we have the fastendpoints package installed, let’s start building up our API application
Update program.cs
First we need to update and add the fastpoints service to the application. We can do this by adding the .AddFastEndpoints to the service container and then using it by adding UseFastEndpoints(); to the app object.
//Add the fastendpoints namespace
using FastEndpoints;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
//add fastendpoint to the service container
builder.Services.AddFastEndpoints();
//add antiforgery
builder.Services.AddAntiforgery();
var app = builder.Build();
//use antiforgery
app.UseAntiforgery();
//use the fastpoints api endpoints
app.UseFastEndpoints();
app.Run();Let’s create a couple of files
Create File (EndpointDemo.cs)
using FastEndpoints;
public class EndpointDemo : Endpoint<DemoRequest, DemoResponse>
{
public override void Configure()
{
Post("/uploaddemo");
//Allow file uploads for this endpoint
AllowFileUploads();
//allow anonymous access to the endpoint
AllowAnonymous();
}
public override async Task HandleAsync(DemoRequest req, CancellationToken ct)
{
//check if we have more than one file uploaded
if ( Files.Count > 0 )
{
//we found files that were uploaded
//get the first file (Demo purposes)
var file = Files[0];
//Write the file name that was uploaded
Console.WriteLine(file.FileName);
}
}
}Create File (DemoRequest.cs)
public class DemoRequest
{
//the file uploaded will bind to this field
public IFormFile File { get; set; }
}Create File (DemoResponse.cs)
public class DemoResponse
{
//define a boolean for the return
public bool Success { get; set; }
}Now that we have the needed parts for the upload API. We can test
From the project directory, execute the watch command
dotnet watch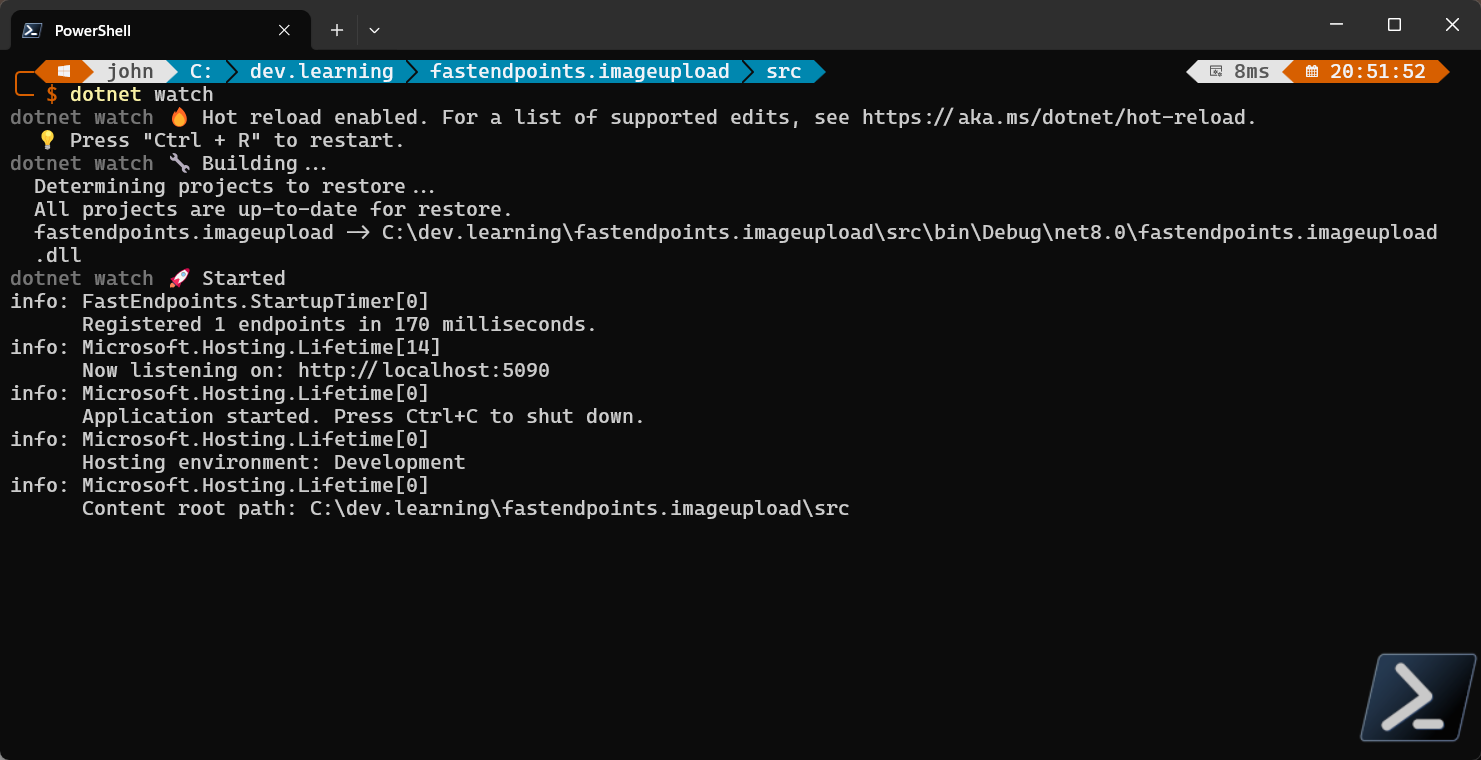
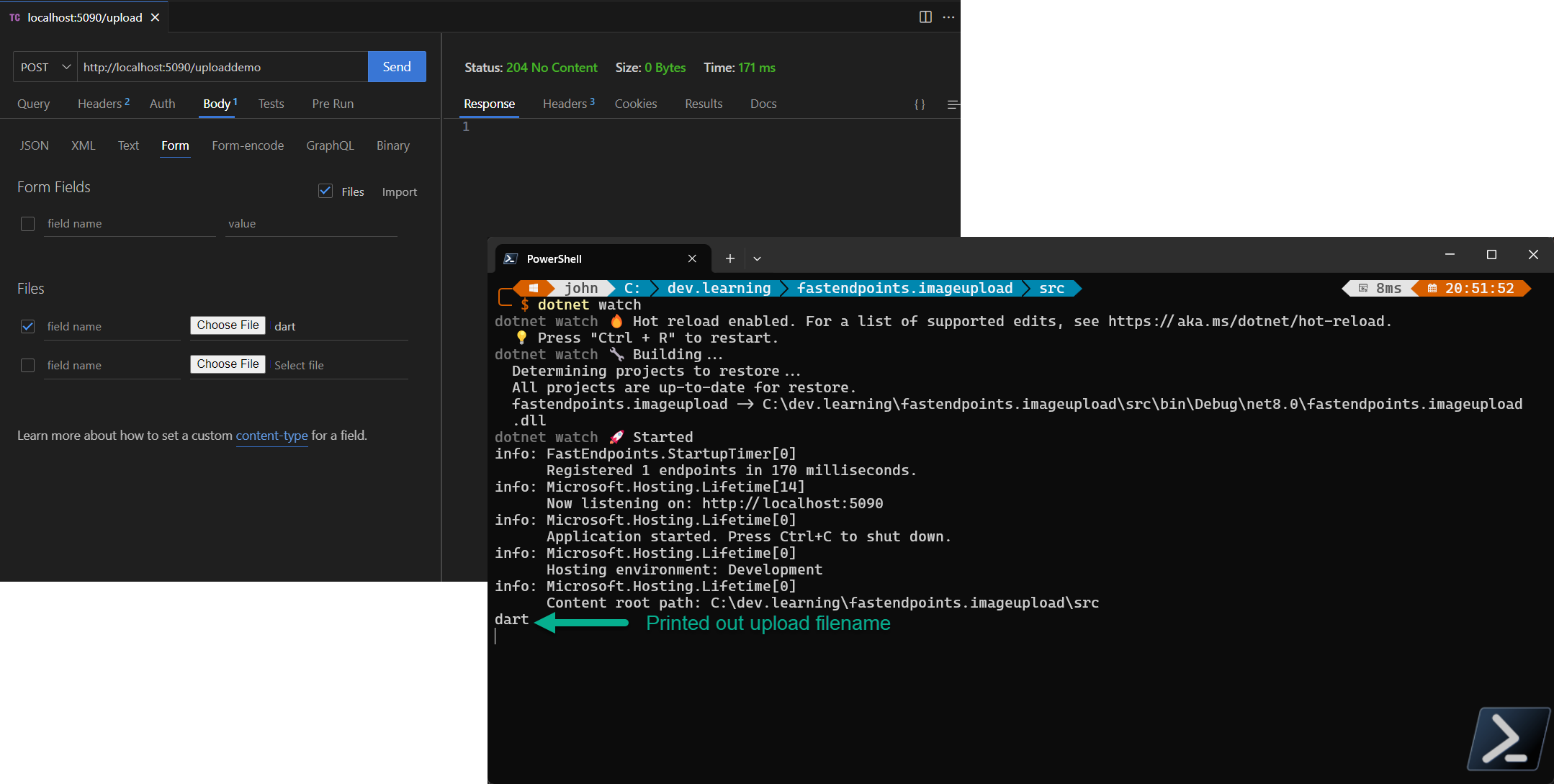
Now that the app is running we can test out the upload API. For this test we are just writing out the filename that is uploaded to the console. We’ll use a API client called thunder client which is integrated into VSCode.
Once you launch Thunder Client from VSCode, create a new request with the following settings
- Request Type: POST
- Request Url: http://localhost:port/uploaddemo
- Body: Check the File Check box.
- Body: Under the files section, select a file you would like to upload
Click the Send button.
Once you execute the request, you will see in the console the filename of the file you uploaded.
Looks good so far, but instead of just printing out the file name, let’s actually write it to a location on the system.
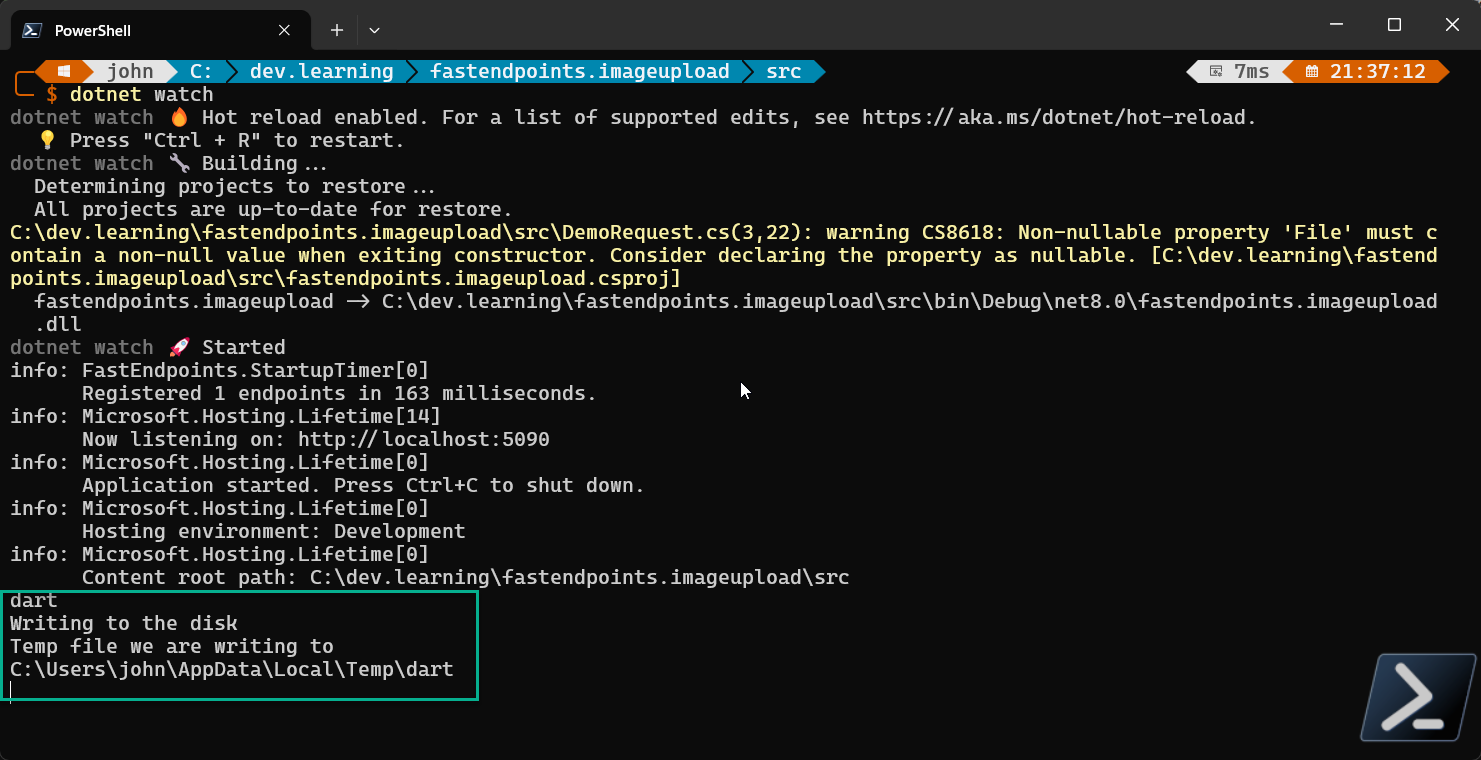
Let’s change the EndpointDemo.cs file to include the following code. It gets the temp file path and appends the filename to it. The it create a stream file and copies the uploaded file into it. VIOLA! We have uploaded a file and stored it on disk
Console.WriteLine("Writing to the disk");
//get the temp file path
var tempFilePath = Path.GetTempPath();
//append the filename to the path
var tempFile = @$"{tempFilePath}{file.FileName}";
Console.WriteLine("Temp file we are writing to");
Console.WriteLine(tempFile);
//write the uploaded file out to the temp location
using (var stream = System.IO.File.Create(tempFile))
{
await file.CopyToAsync(stream);
}
This is just a basic example for file uploading with fastendpoints. Remember you should secure your endpoints with some type of authentication/authorization. Also when it comes to uploaded file, think about things like limiting the file size, number of files that can be uploaded, DDOS attackes etc.